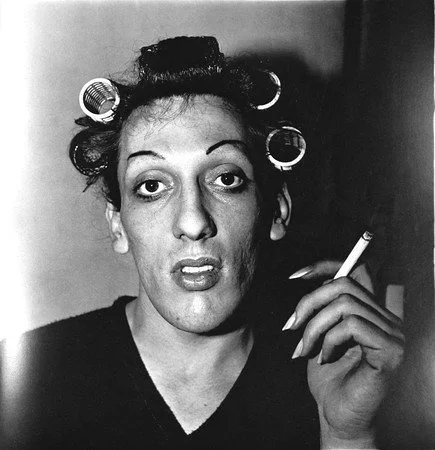
Diane Arbus’s photographs are not for the faint of heart. They are unsettling, often disturbing, yet undeniably compelling. They are portraits of the marginalised, the eccentric, the “freaks” as they were often labelled, but also of the seemingly ordinary – the suburban housewife, the child in its Sunday best. Arbus’s lens doesn't simply record; it probes, it questions, it forces us to confront our own preconceptions about normality and otherness. Her work, one could argue, is a kind of visual anthropology of the American condition, a sometimes brutal, sometimes tender, but always unflinching examination of the human psyche. As Susan Sontag wrote, “Arbus’s photographs are… about the secret life of America.” They are, to my mind, less about the what and more about the why – why we look, why we categorise, why we recoil or connect with the figures in her frames. As Arbus herself said, “I don’t press the shutter. The image does, and it’s like being gently clobbered.” It's a powerful description of her process, the sense of being overtaken by the image itself.
Arbus’s influences are complex and not always easily discernible. She studied with Berenice Abbott, Alexey Brodovitch, and Lisette Model, formative experiences that undoubtedly shaped her approach to photography. She encountered the works of Mathew Brady, Paul Strand, and Eugène Atget early on, visits made with her then-husband, Allan Arbus. These early encounters undoubtedly shaped her understanding of photography’s potential. While she admired the work of Weegee, the tabloid photographer known for his graphic images of crime scenes and urban life, her approach was fundamentally different. Weegee’s photographs are often sensational, focused on the dramatic moment. Arbus, on the other hand, was interested in the quieter, more subtle aspects of human experience. She sought to capture the inner lives of her subjects, their vulnerabilities, their anxieties, their hidden selves. “A photograph is a secret about a secret,” Arbus once said. “The more it tells you the less you know.” This sense of mystery, this feeling of something unsaid, is a hallmark of her work.
Her early work, including her commercial work with her husband, honed her technical skills and her eye for composition, but it was her personal work, her exploration of the city and its inhabitants, that truly defined her. She photographed circus performers, transvestites, and other individuals who lived on the fringes of society. These early images, while already displaying her distinctive style, are often more straightforwardly descriptive. Later, her work became more introspective, more focused on the psychological dimensions of her subjects. She began to use a Rolleiflex camera, which allowed her to get closer to her subjects and to capture their expressions with greater intimacy. This shift in technique coincided with a deepening of her artistic vision. She moved beyond simply documenting the “other” and began to explore the ways in which we all perform our identities, the masks we wear to navigate the world. “I really believe there are things nobody would see if I didn't photograph them,” she asserted. It's not just about the subject, but the relationship between photographer and subject, the implicit contract of looking. As she further noted, “For me the subject of the picture is always more important than the picture. And more complicated.”
Arbus’s photographs are not always comfortable to look at. They can be disturbing, even shocking. But they are also deeply human. They remind us of our own vulnerabilities, our own anxieties, our own sense of being different. She had a knack for capturing the awkwardness, the fragility, the sheer strangeness of human existence. “I’m always interested in people who represent themselves in a certain way,” she explained. “It’s like a mask that they put on. It’s a way of dealing with the world.” And it is these masks, these carefully constructed personas, that Arbus’s camera penetrates, revealing the humanity beneath.
Her inclusion in the Museum of Modern Art’s “New Documents” exhibition in 1967, alongside Garry Winogrand and Lee Friedlander, marked a turning point in her career, though her work was already evolving in this direction. This exhibition, which highlighted a new generation of photographers who were challenging traditional notions of documentary photography, placed Arbus’s work in a broader context and helped to solidify her reputation as a significant artist. Her two Guggenheim Fellowships in the 1960s also provided crucial support for her work.
Her 1972 retrospective at the Museum of Modern Art in New York, a year after her death by suicide, cemented her place in the history of photography. It was a controversial exhibition, with some critics accusing her of exploitation and voyeurism. But it was also a hugely influential exhibition, introducing her work to a wider audience and sparking a debate about the nature of photography and its relationship to reality. Her work was also shown at the Venice Biennale, a rare honour for a photographer. Since then, numerous exhibitions, including major retrospectives like “Diane Arbus Revelations” and “in the beginning,” have further explored and contextualised her work, revealing the depth and breadth of her artistic vision.
Arbus’s book, Diane Arbus: An Aperture Monograph, published posthumously, has become a classic of photographic literature. It features many of her most iconic images, accompanied by her own writings and reflections on her work. The book offers a glimpse into her creative process, her motivations, and her unique way of seeing the world. The acquisition of her complete archive by the Metropolitan Museum of Art in 2007 has ensured that her work will continue to be studied and appreciated for generations to come. The ongoing publication of books and catalogues, such as Diane Arbus Documents, further demonstrates the continuing fascination with her work and its evolving interpretation.
Arbus’s work fits into a broader context of 20th-century art that explored the themes of alienation, identity, and the human condition. Her photographs share a certain kinship with the work of artists like Edward Hopper, whose paintings depict the isolation and loneliness of modern life. They also resonate with the work of photographers like Robert Frank, whose book The Americans offered a similarly unflinching portrait of American society. “My favourite thing is to go where I’ve never been,” Arbus declared. And it is this spirit of exploration, this willingness to venture into the unknown, that defines her art.
Arbus’s influence on subsequent generations of photographers is undeniable. Her work has paved the way for a more subjective and personal approach to photography, one that embraces the complexities and contradictions of human experience. Photographers like Nan Goldin, Sally Mann, and Joel-Peter Witkin, each in their own way, owe a debt to Arbus’s pioneering vision.
Diane Arbus’s legacy is complex and multifaceted. She is remembered as a photographer who dared to look where others wouldn't, who challenged our notions of beauty and normality, and who revealed the hidden truths of the human heart. Her photographs continue to fascinate, to disturb, and to inspire. They are a testament to the power of photography to illuminate the darkest corners of the human psyche and to remind us of our shared humanity, even in our most vulnerable and imperfect moments. As Janet Malcolm wrote, "Arbus's photographs are not about freaks. They are about us." And it is this unflinching self-portrait, this unflinching look at ourselves through the lens of Diane Arbus, that constitutes her enduring legacy.