William Klein, a name synonymous with a raw, visceral, and often confrontational style of street photography, remains a pivotal figure. He wasn’t interested in the polite, the picturesque, or the perfectly composed. Instead, he embraced the chaotic energy of urban life: the blur, the grain, the awkward angles, and the sheer messiness of the world. His work, particularly his early street photography, crackles with a restless energy, a sense of immediacy that continues to resonate. He wasn’t a detached observer, but an active participant, his camera a weapon, a tool for exploration, and a means of engaging with the world on his own terms. “I was a kind of anti-photographer,” Klein once said, “I was going against all the rules.” This rebellious spirit is evident in every frame. As he later reflected, “I’m an outsider, I guess. I wasn’t part of any movement. I was working alone, following my instinct. I had no real respect for good technique because I didn’t know what it was. I was self-taught, so that stuff didn’t matter to me.”
Klein’s influences are complex and, perhaps characteristically, somewhat contradictory. He wasn’t formally trained as a photographer. His background was in painting, studying with Fernand Léger in Paris. This artistic foundation undoubtedly shaped his visual approach, giving him a keen sense of composition, even when seemingly abandoning traditional rules. Léger, as Klein recalled, “told us not to worry about galleries and collectors, but to go out onto the city streets and paint murals.” It was while photographing some of his interior murals, “big hard-edged geometrical paintings,” that Klein had an epiphany. “Somebody turned one of the panels when I was shooting on a long exposure, and when I developed the photographs this already abstract shape was a beautiful blur. That blur was a revelation. I thought, here’s a way of talking about life. Through photography, you can really talk about what you see around you. That’s what I’ve been doing ever since.” One can see echoes of the bold lines and dynamic forms of Léger's work in Klein’s own compositions, albeit translated into the language of photography. However, Klein’s real education came from the streets, from the raw energy of New York City in the 1950s. He cites Weegee, the tabloid photographer known for his gritty depictions of crime scenes and urban life, as a key inspiration. “Weegee showed me that photography could be tough,” Klein said. But Klein’s work goes beyond Weegee’s sensationalism. He adds a layer of social commentary, a sense of irony, and a distinctly modern aesthetic.
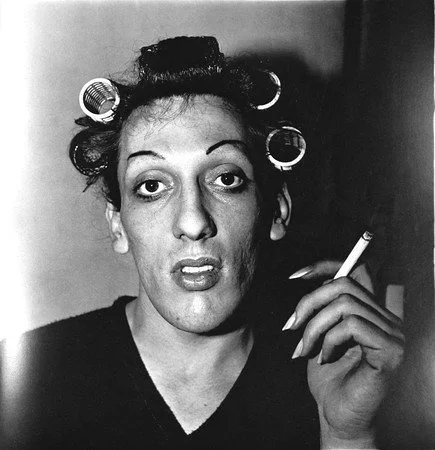
What sets Klein apart is his unflinching gaze, his willingness to confront the viewer with the raw reality of urban existence. His photographs are often confrontational, sometimes even aggressive. They capture the chaos, the noise, the sheer overwhelmingness of city life. In his iconic series “Life is Good & Good for You in New York,” the city becomes a stage for a kind of urban theatre, populated by characters who are both ordinary and extraordinary. The images are often close-up, sometimes blurred, capturing fleeting moments of interaction, expressions of joy, despair, and everything in between. “I wanted to show the city as I saw it,” Klein explained, “not as it should be.” This desire to capture the unvarnished truth, to embrace the imperfections and contradictions of urban life, is what makes his work so powerful. He wasn’t interested in creating a sanitised version of reality, but rather a visceral and immediate experience of the city. As he put it, “People said, ‘What a put-down — New York is not like that. New York is a million things, and you just see the seamy side.’” His view of New York, as he confessed, was that it was “like a big shithouse.”
Klein’s work evolved over the course of his career, moving beyond the raw immediacy of his early street photography. He ventured into fashion photography, bringing his distinctive style to the pages of Vogue. Even in this commercial context, he retained his rebellious spirit, pushing the boundaries of the genre. His fashion photographs are often dynamic, energetic, and sometimes even humorous, a far cry from the static and posed images that were typical at the time. He used wide-angle lenses, unusual perspectives, and blurred motion, creating a sense of immediacy and excitement. As Dorothy McGowan, a Vogue model who worked with Klein, recalled, “People were terrified of him, as though it was the lion’s den.” Klein himself acknowledged, “They were probably the most unpopular fashion photographs Vogue ever published.” This willingness to experiment and to challenge conventions is a hallmark of Klein’s work, regardless of the subject matter. He even made a film about the fashion world, “Who Are You, Polly Maggoo?”, which, as he recalled, “was completely foreign to the whole movie scene here in France.” Later, he made documentaries on figures like Muhammad Ali and Little Richard, drawn, as he said, to “great characters.”
His books are as important to his oeuvre as his individual photographs. “Life is Good & Good for You in New York,” published in 1956, is considered a landmark in the history of photobooks. Its raw energy, its unconventional layout, and its unflinching portrayal of urban life made it a radical departure from the prevailing aesthetic of the time. The book itself becomes a kind of extension of Klein’s photographic practice, a dynamic and immersive experience for the viewer. Other notable books include “Tokyo” (1964) and “Moscow” (1964), both of which capture the unique character of these cities through Klein’s distinctive lens. These books are not simply collections of photographs; they are visual essays, capturing the spirit and energy of a place. As he described his approach to his books, “The sequencing of the New York book, and even the composition of individual images, also seems to owe something to comic-books.” His first book, however, met with resistance. “They just didn’t get it,” he said of the initial reaction to “Life is Good & Good for You in New York.” “They thought it should not have been published, that it was vulgar and somehow sinned against the great sacred tradition of the photography book. They were annoyed for sure.”
Klein’s exhibitions have also played a significant role in shaping his reputation. His work has been shown in major museums and galleries around the world. One particularly important exhibition was his retrospective at the International Center of Photography in New York in 1996. This exhibition brought together a wide range of his work, from his early street photography to his fashion work and his films, providing a comprehensive overview of his career. It highlighted the diversity of his practice and his consistent willingness to challenge conventions. Even in his exhibitions, Klein sought to create a dynamic and engaging experience for the viewer, reflecting the energy and immediacy of his photography. More recently, a joint retrospective with Japanese photographer Daido Moriyama at Tate Modern explored the similarities in their depictions of New York and Tokyo. Klein, however, remained characteristically nonchalant about the exhibition. “I think it’s kind of stupid,” he said, shrugging, “but a lot of things happen without me really being involved. There’s a connection all right, but…”
Klein’s work sits squarely within the tradition of street photography, but it also transcends it. He shares with photographers like Henri Cartier-Bresson a fascination with the decisive moment, but his approach is radically different. While Cartier-Bresson sought to capture the perfect composition, the harmonious balance of form and content, Klein embraced the chaos and the unpredictability of the street. His work is more akin to that of Robert Frank, whose book “The Americans” also challenged the conventions of the time, but Klein’s work has a distinct energy, a sense of urgency that is all his own. “I’m not a documentarian,” Klein has said. “I’m an artist. I’m interested in my own vision of the world.”
Klein’s influence can be seen in the work of many photographers who followed. His bold use of composition, his willingness to embrace the imperfections of the medium, and his unflinching portrayal of urban life have all had a lasting impact. While it's difficult to pinpoint specific individuals, his influence is more pervasive, a kind of spirit of rebellion that encourages photographers to break the rules, to challenge conventions, and to find their own unique voice. He showed that photography could be more than just a record of reality; it could be a powerful means of expression, a way to engage with the world on a personal and visceral level.
William Klein’s legacy is one of innovation, experimentation, and a relentless pursuit of his own vision. He wasn’t afraid to challenge the established norms of photography, to push the boundaries of the medium, and to capture the world as he saw it, in all its messy, chaotic, and often beautiful complexity. His work continues to inspire and provoke, reminding us that photography can be a powerful tool for exploring the world around us and for engaging with the human experience in all its richness and diversity. He showed us that the streets can be a gallery and that life itself is the greatest subject of all. As Orson Welles said of Klein’s film “Broadway by Light,” “the first film I've seen in which colour was absolutely necessary.” This sense of innovation and pushing boundaries is a hallmark of Klein’s entire oeuvre, from his early street photography to his fashion work and his films.